_____ AI in Marketing Statistics
The Latest AI in Marketing Facts & Stats For 2026
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping the marketing landscape, moving from experimental tool to essential strategy driver. As a result, it is vital that every marketer learns about this powerful new technology and how it can be harnessed to help them deliver more effective marketing campaigns.
In fact, exclusive data collected by our GEO agency team for this report shows that the average annual salary for roles that mention AI in their job descriptions are 20.26% higher than those roles that lack any reference to this growing technology in the job description:
From automating campaign insights to transforming customer experiences and helping marketers deliver effective GEO audits, AI adoption rates are climbing across industries, yet the path forward isn’t without obstacles. Marketers face challenges around implementation, data security, and team adaptation as they work to harness AI’s potential.
The rise of generative AI is disrupting one of marketing’s core pillars: search engine marketing. With the emergence of generative search engines, businesses must rethink how they approach visibility and relevance, ushering in a new era of generative engine optimisation (GEO).
In this research piece, we will explore the latest statistics on AI in marketing, the barriers teams encounter, how organisations are evolving, and what the shift towards AI-driven search means for the future of digital marketing.
Top 10 AI in marketing and GEO stats
- Exclusive Reboot data shows marketing roles mentioning AI pay 20.26% more on average than roles without AI requirements.
- Nearly two-thirds (64.5%) of marketers say that AI impacts content creation and copywriting the most, exceeding the next highest task by 20 percentage points.
- Only 5.2% of marketers say they see no value in AI or have not tried AI tools.
- Four-fifths (82%) of marketers say their main priority with AI is reducing time on repetitive, data-driven tasks.
- More than half (54.2%) cite inaccurate or inconsistent AI output as the biggest limitation, showing quality concerns remain the top barrier even as usage grows.
- 41% identify data privacy concerns as the biggest barrier to adopting new AI tools.
- 53% of marketing professionals think AI will eliminate more jobs than it creates in the next three years, despite very few teams (4.5%) reporting downsizing.
- Over three-quarters (77%) of ChatGPT users now use it as a search engine, signalling a major shift away from traditional search behaviour.
- Branded web mentions show the strongest correlation with appearing in AI search overviews, much higher than backlinks, domain rating, or ad spend.
[Exclusive data] Does AI impact marketing salaries?
Search marketing agency Reboot Online undertook exclusive research to determine whether marketing roles that highlight the need for AI skills are paid at a higher or lower salary than ‘traditional’ marketing and SEO roles.
Average salaries of marketing roles

| Role | Average salary of roles mentioning AI (£) | Average salary of roles not mentioning AI (£) |
|---|---|---|
| Other Marketing | 49,150.22 | 39,841.60 |
| Social | 48,283.36 | 39,623.74 |
| Content | 51,454.71 | 44,173.19 |
| PR/Comms | 50,856.68 | 42,165.85 |
| SEO | 49,383.96 | 39,204.18 |
| Performance/PPC | 47,326.98 | 44,743.61 |
| Creative/Design | 46,117.29 | 39,199.80 |
| General Marketing | 45,726.73 | 34,592.13 |
(Source: Reboot Online)
Analysis of nearly 7,600 roles in the marketing sector, including social, content, SEO, PPC, and more, reveals that across all roles, those that mention AI in their job descriptions offer higher salaries than those that don’t.
On average, marketing roles that mention AI in their descriptions are paid 20.26% higher salaries than those that lack any reference to the growing technology.
The greatest difference in remuneration is found in general marketing roles, where those that specify AI and related terms in their descriptions are paid 32.19% more than those that do not.
How is AI used in marketing?
What tasks do marketers use AI for?
Content creation and copywriting is far and away the task where marketers have seen AI’s greatest impact. Nearly two-thirds of those surveyed have noted a tangible impact from leveraging the technology in this area.
Writing effective content is integral to a brand’s performance. Reboot Online’s eCommerce SEO statistics report found that 52% of eCommerce pages were either very easy or fairly easy to read. By leveraging AI’s content writing and editorial skills, brands and SEO agencies can further improve their readability.
AI’s most valuable marketing tasks, according to professionals

| Task | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Content creation and copywriting | 64.5 |
| SEO and content optimisation | 43.9 |
| Brainstorming and idea generation | 43.9 |
| Research | 33.5 |
| Overall productivity and efficiency | 23.2 |
| Analytics, insights, and attribution | 14.8 |
| Email marketing and automation | 12.9 |
| PPC and paid media campaign optimisation | 9.7 |
| CRM: Customer segmentation, lead scoring, and nurturing | 5.2 |
| Customer experience and chatbots | 3.9 |
| Video content creation | 3.2 |
| Personalisation at scale | 3.2 |
| Social listening and sentiment analysis | 1.9 |
(Source: Search Engine Journal)
SEO and content optimisation, as well as brainstorming and idea generation, saw the second-biggest impact, according to 43.90% of marketers. Though these are the second-most popular tasks for AI use, 31.94% fewer professionals have made use of AI in this area than for content creation and copywriting (43.9% vs. 64.5%).
Only 5.2% of marketers surveyed answered that they either see no value in AI or have not experimented with AI tools yet. Nevertheless, this indicates that one in 20 marketing professionals is not keeping up with technological advancements.
What are the most popular types of AI tools in marketing?
Among marketing professionals who use AI in their roles, general-purpose chatbots and image or design generators are the most popular AI tools, with each being utilised by two-fifths of marketers.
The popularity of chatbots supports the data that content creation and copywriting are the most common tasks that professionals utilise AI for.
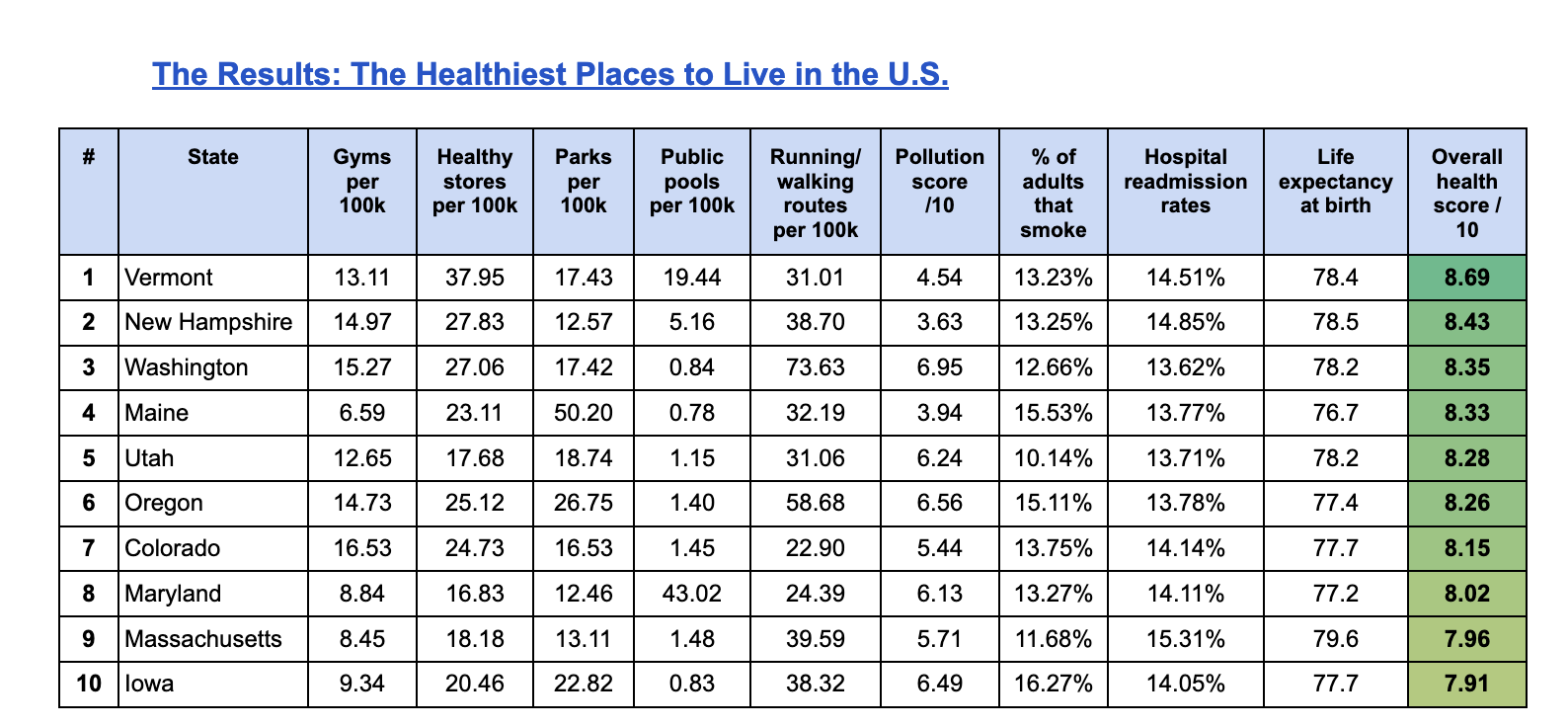
AI tools used by professionals in their marketing roles in the last year
| Type of tool | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| General-purpose chatbots | 40 |
| Image or design generators | 40 |
| SmartAI video or audio editing AI tools | 36 |
| Voice or narration generators | 33 |
| Smart/AI image editing tools/features | 33 |
| Video or animation generators | 30 |
| General-purpose text generation tools | 27 |
| AI web design and/or code generators | 24 |
| AI-enhanced productivity tools | 21 |
| Non-voice audio generators | 19 |
(Source: HubSpot)
One of the benefits cited by many AI adopters is its productivity gains, with a fifth of marketers using specific AI-enhanced productivity tools. The productivity wins noted by marketing professionals then appear to be a result of integrating AI across the board, rather than through particular time-management processes.
So, whether you are a AiPR agency looking to run more productive campaigns and earn more brand mentions for your clients, a digital PR agency focused on earning more backlinks, or a GEO and AIO company wanting to streamline your audits, you should be leveraging AI to drive efficiency and productivity gains across your processes.
The most popular AI chatbots used by marketers
With chatbots being the most popular AI tool leveraged by marketers, there is a clear market dominance by one chatbot in particular.
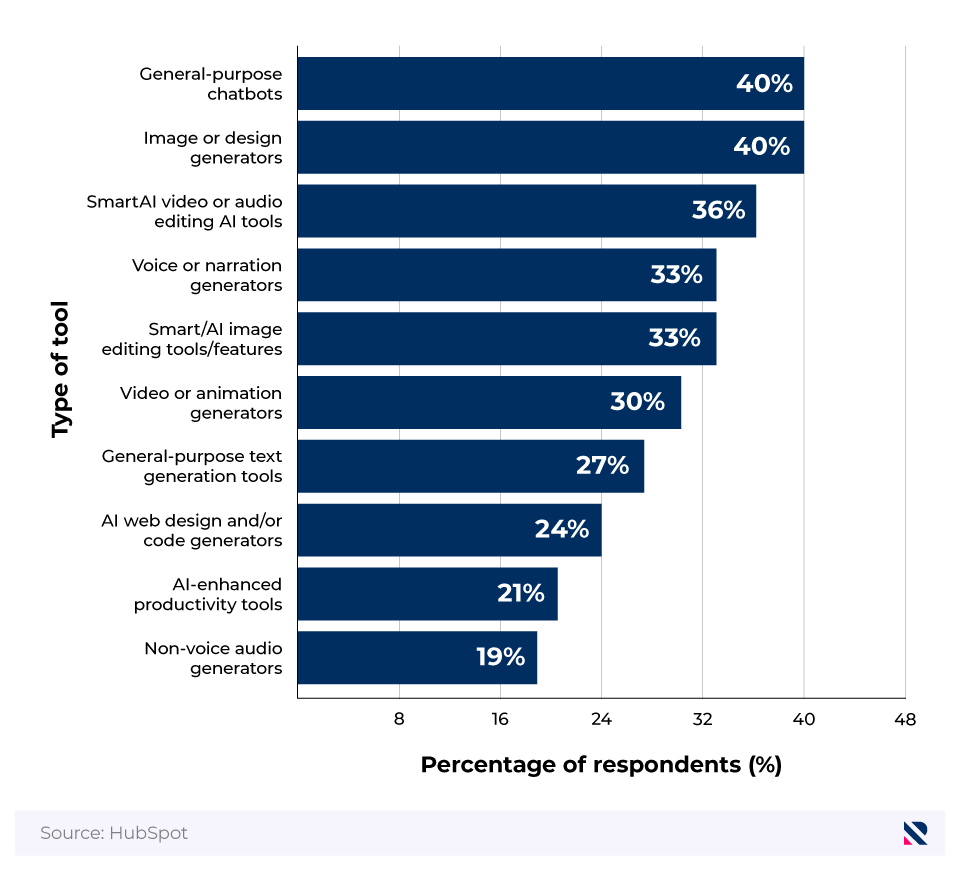
Chatbots used by professionals in their marketing roles
| Chatbot | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 88 |
| Google Gemini | 52 |
| Microsoft Copilot | 44 |
| Meta AI assistant | 28 |
| Deepseek | 17 |
| Claude | 11 |
| Perplexity | 10 |
(Source: HubSpot)
Nearly nine in 10 professionals who have adopted AI use ChatGPT, 69.23% more than those who use Google Gemini (88% vs. 52%).
The sustained popularity of ChatGPT is evidence of the power of being an early experimenter with new technology. One of the first chatbots introduced, ChatGPT, still leads the market, and these lessons also apply to marketing professionals who readily experiment and adopt AI over those who don’t.
What do marketers hope to achieve by leveraging AI?
Among marketing individuals and teams who have begun leveraging AI, the number one desired outcome of adoption is reducing time spent on repetitive tasks.
Over four-fifths of those surveyed stated that this is one of the primary outcomes they’re interested in achieving with the technology.
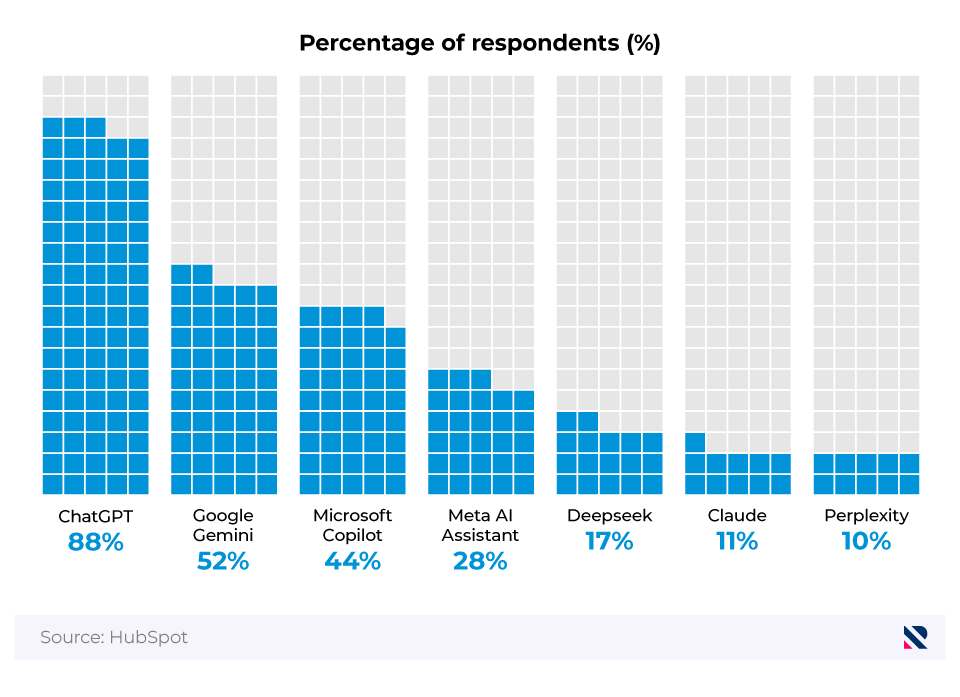
The primary outcome that marketing organisations are interested in achieving with AI
| Outcome | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Reduce time spent on repetitive, data-driven tasks | 82 |
| Get more actionable insights from marketing data | 65 |
| Accelerate revenue growth | 63 |
| Unlock greater value from marketing technologies | 59 |
| Generate greater ROI in campaigns | 58 |
| Create personalised consumer experiences at scale | 56 |
| Drive costs down | 52 |
| Increase qualified pipeline | 43 |
| Predict consumer needs and behaviours with greater accuracy | 43 |
| Shorten the sales cycle | 32 |
| Other | 6 |
| None of the above | 1 |
(Source: Marketing AI Institute and SmarterX)
Professionals’ desired outcomes are indicative of the wide-ranging expectations of AI tools. From financial results, including greater ROI and lower costs, to scheduling impacts, such as a shorter sales cycle and accelerated growth, businesses that have adopted AI expect positives across the entirety of their operations.
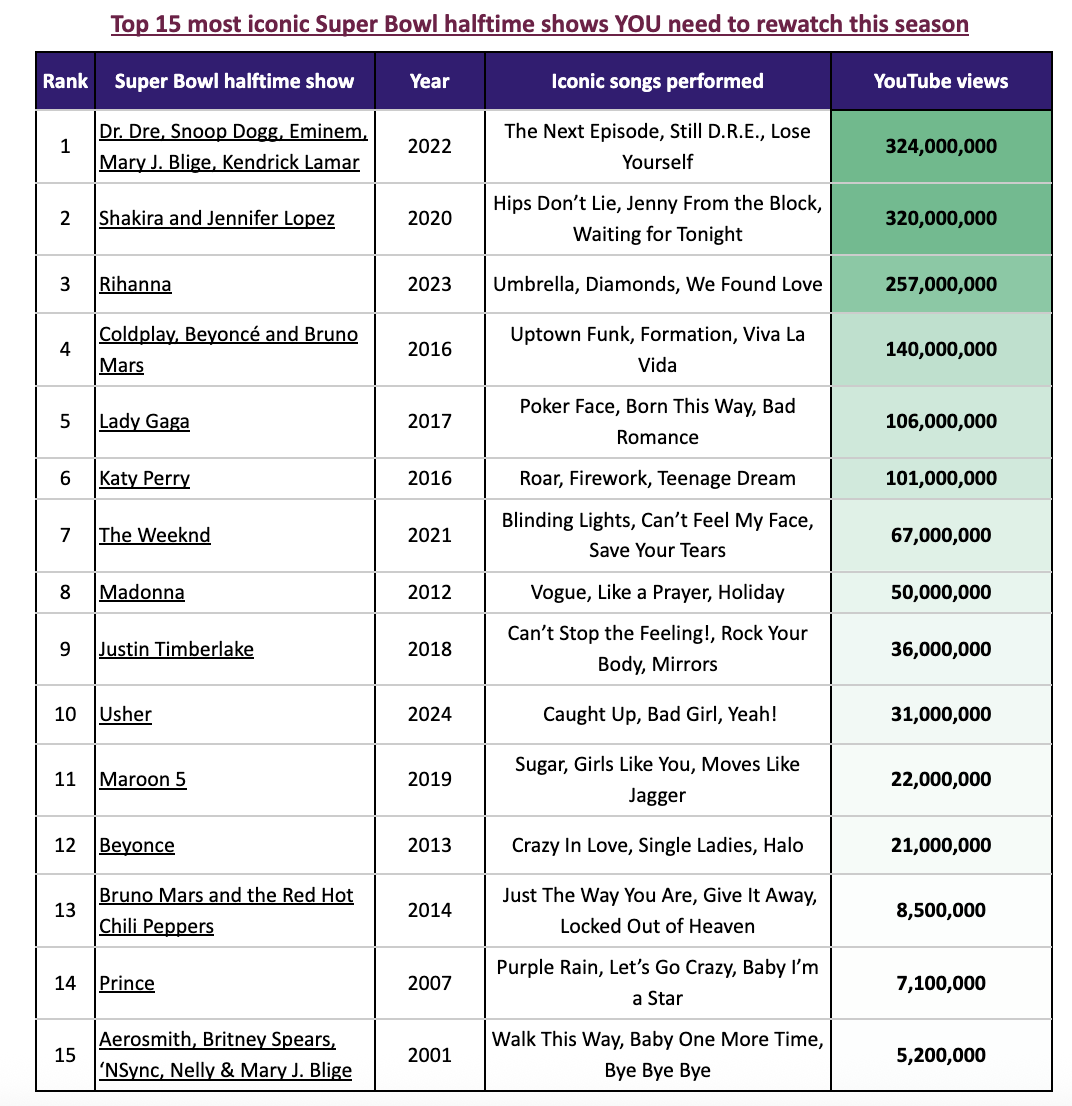
How do marketing professionals measure AI effectiveness?
AI adoption is an exercise in experimenting and making adjustments to how it’s used, and measuring effectiveness is a key stage in this process.
How marketing professionals measure the effectiveness of AI tools in their strategy
| Measure | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Increased productivity | 64 |
| Time saved across teams | 55 |
| Better overall role performance | 43 |
| Better personalisation for customers | 39 |
| Enhanced data insights | 39 |
| Improved ROI of projects where AI was used | 37 |
| Positive feedback from colleagues or clients on projects or processes where AI was used | 22 |
(Source: HubSpot)
Nearly two-thirds of professionals state that increased productivity is the biggest signifier of an AI tool’s effectiveness. Similarly, 55% of marketers are looking for time saved on tasks as a tangible impact of AI adoption.
While two-fifths of professionals are interested in an improved return on investment on AI-enhanced products, this measure is less important to teams than better overall role performance and the associated time and productivity gains.
Future of AI in Marketing: Opinions and impact
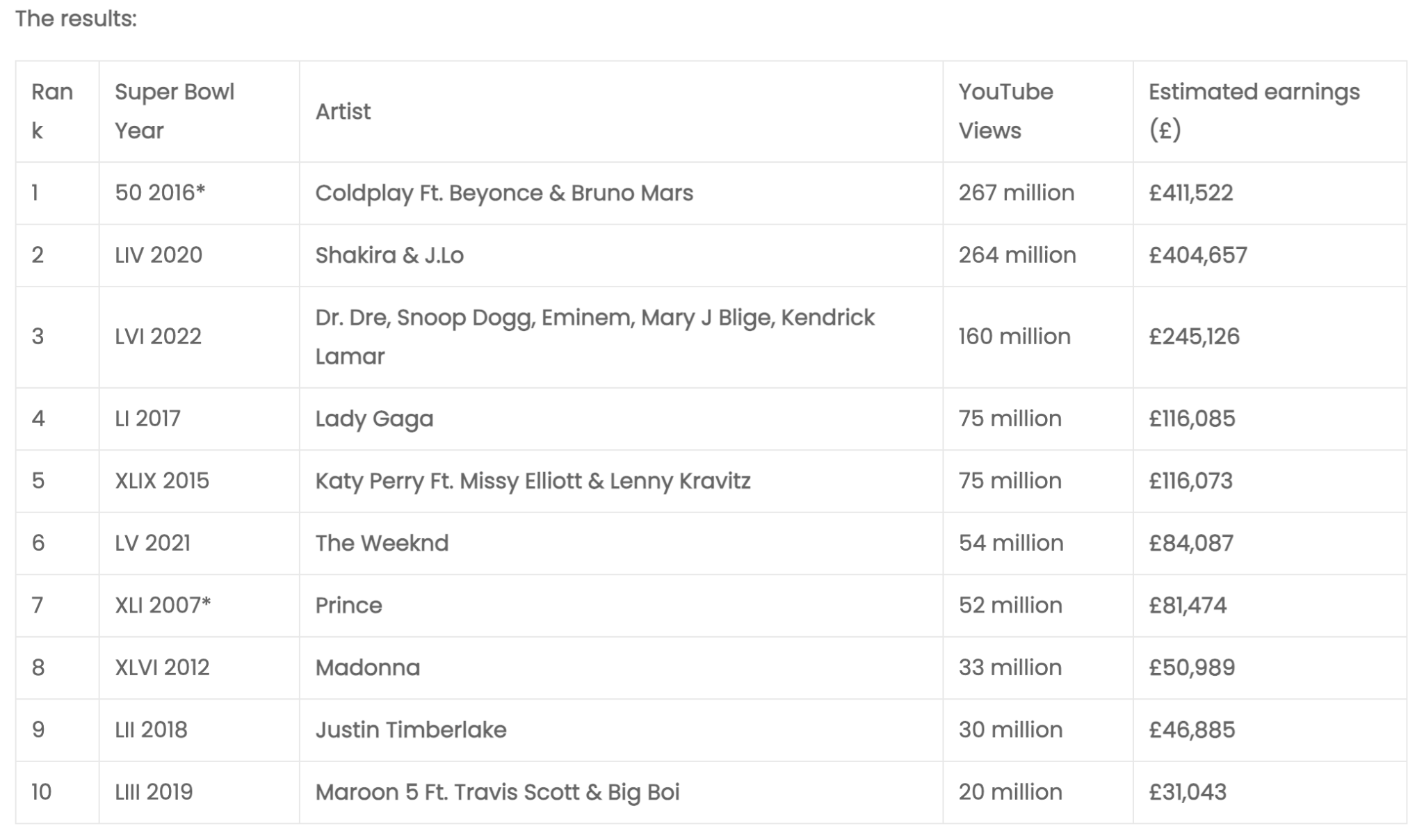
What are the limitations of AI in marketing?
The quality of AI output is still a major concern for marketing professionals, with over half noting that the greatest limitation they have encountered with AI is its inaccurate, unreliable, or inconsistent output quality.
This limitation has been dubbed AI hallucination - incorrect or misleading information presented as fact.
The way in which AI models are built is what causes these hallucinations, since they are designed to predict the next most likely token and not actually understand the truth underlying the topic at hand and/or generating content about.
Despite the best large language models generating incredibly accurate responses in most cases, even a slim chance that they will generate incorrect, inaccurate and even potentially harmful responses in the rarest of circumstances means that they can not be 100% relied upon.
These concerns highlight a key consideration among marketing professionals - despite its benefits, AI nevertheless needs substantial human oversight to be used effectively.
Greatest limitations and inefficiencies encountered by professionals when using AI in marketing
| Limitation | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Inaccurate, unreliable, or inconsistent output quality | 54.2 |
| Limited ability to understand context or nuance | 32.3 |
| Requires too much manual review or editing | 22.6 |
| Difficult to integrate with existing tools or processes | 18.1 |
| Legal, privacy, or data compliance concerns | 16.1 |
| Lack of brand voice consistency | 16.1 |
| Lack of citation and source attribution | 14.8 |
| Expectations don't meet reality | 13.5 |
| Steep learning curve or requires upskilling | 12.9 |
| Wasted time or budget on ineffective tools | 3.9 |
(Source: Search Engine Journal)
The need for human input is apparent in other limitations of AI. Over a fifth of marketers said that AI requires too much manual review and editing, while 16.1% noted that AI is unable to maintain brand voice in its output consistently.
Many of the limitations and inefficiencies highlighted by marketing professionals are related to the first step in adopting and integrating AI. Nearly a fifth noted that they have struggled to integrate the technology with existing tools, while 16.1% have raised legal, privacy, and data compliance concerns as a blocker to working with AI.
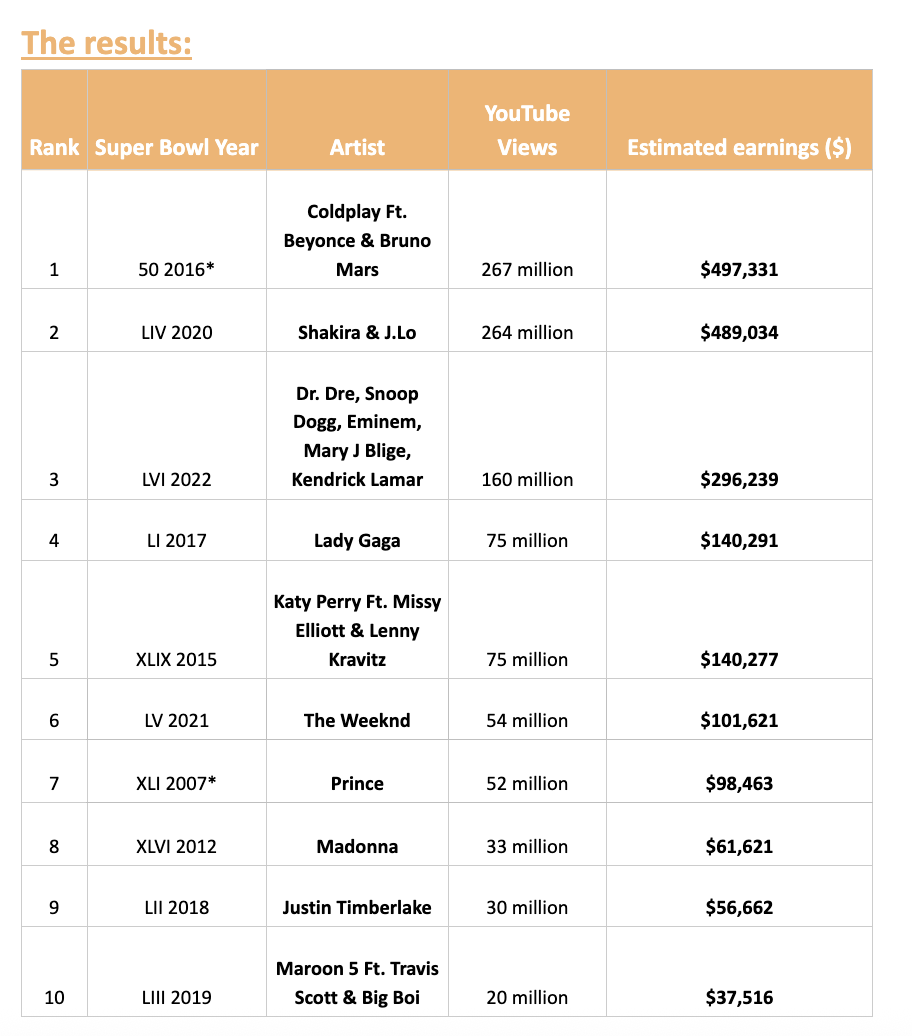
What are the barriers to introducing AI into marketing roles?
In line with the limitations related to legal, privacy, and data compliance concerns noted above, the greatest barrier to adopting AI tools among marketing professionals is data privacy concerns.
These include concerns around the potential sharing of data without consent and the risk of security breaches.
Greatest barriers to adopting new AI tools in the past year
| Barrier | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Data privacy concerns | 41 |
| Training and time investment | 39 |
| Too many new tools that do similar things but don't connect to one another | 34 |
| Integration challenges with existing or legacy systems | 34 |
| I/my teammates prefer to use a different tool than what our company invests in | 27 |
| Resistance to change within the organisation | 27 |
| Role security concerns | 26 |
| Ethical or legal compliance concerns | 22 |
(Source: HubSpot)
Nearly two-fifths of professionals surveyed stated that the training and time investment required to get their teams proficient in AI tools is one of the greatest barriers to adoption.
This reluctance to spend time and money on training is likely to impact marketing teams’ growth, as others upskill and offer new services such as AiPR and GEO audits.
How have marketing team structures been affected by AI?
The majority (42.6%) of marketing teams have not undergone any significant structural changes to facilitate AI adoption.
Ways in which marketing team structures have evolved to accommodate AI implementation

| Action | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| No significant structural changes | 42.6 |
| Upskilled existing team members | 37.4 |
| Other | 5.8 |
| Reorganised teams around AI capabilities | 5.2 |
| Reduced the marketing team | 4.5 |
| Partnered with external AI specialists | 2.6 |
| Created new specialised AI roles | 1.9 |
(Source: Search Engine Journal)
A slightly smaller proportion of teams have focused on upskilling existing team members to promote AI proficiency. This option has been significantly more popular than opting to partner with external AI specialists.
Aside from restructuring, some teams have reduced or expanded their teams to make way for AI. Under one in 20 teams have reduced the size of their marketing team to accommodate AI implementation, while 1.9% have created new specialised AI roles.
Impact of AI on marketing jobs
Over half of the professionals surveyed believe that the net effect of AI will mean more jobs are eliminated in the next three years.
At present, 4.5% of current marketing teams have downsized due to AI, but there is an industry expectation that this will accelerate.
Research from the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis reports that occupations with higher AI exposure experienced larger unemployment rate increases between 2022 and 2025. As marketing departments increase their AI adoption, this may place the industry at risk of further layoffs.
Marketing professionals’ perspective on the net effect of AI on marketing jobs over the next three years

| Effect | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| More jobs will be created by AI | 24 |
| More jobs will be eliminated by AI | 53 |
| AI won't have a meaningful impact on jobs | 7 |
| I don't know | 15 |
*Figures do not add up to 100% due to source rounding.
(Source: Marketing AI Institute and SmarterX)
Nearly a quarter of professionals believe that AI will have a positive effect on the marketing industry, ultimately creating more jobs over time. Although the data presented above indicates a focus on restructuring rather than growing teams, this trend may change in time as teams look to hire more AI specialists.
Consumer insights: AI in Search
How many people use ChatGPT as a search engine?
Over three-quarters (77%) of those who use ChatGPT use the tool as a search engine.
What do people search for using ChatGPT?
Among those who use ChatGPT as a search engine, conversational, everyday questions are their most common searches. Well over half of those surveyed reported using the chatbot for this type of query.
Most popular types of searches made using ChatGPT

| Type of search query | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Everyday questions | 55 |
| Brainstorming or creative inspiration | 53 |
| Work-related tasks | 43 |
| Fact-checking | 42 |
| Product research | 34 |
| Recipes or cooking ideas | 30 |
| Tech troubleshooting | 29 |
| Career or interview prep | 26 |
| Schoolwork or studying | 23 |
| Travel planning | 23 |
| Entertainment recommendations | 22 |
| Mental health advice | 22 |
| Financial or investing advice | 21 |
| Online shopping | 13 |
| Dating or relationship advice | 11 |
| Discovering new brands | 8 |
(Source: Adobe Study)
Further, more than half of ChatGPT users use the tool for brainstorming and creative inspiration.
While over two-fifths of users make use of the tool for work-related tasks, only half of these users are using the tool for schoolwork and studying.
People are also turning to ChatGPT for advice, with over a fifth of users seeking mental health, financial, and investing advice.
However, these use cases present risks, with research from a partnership between King’s College London, the Association of Clinical Psychologists UK, and the Guardian suggesting that ChatGPT fails to identify risky behaviour when in conversation with those with mental health problems.
In response to these concerns, OpenAI stated in October 2025 that it had strengthened ChatGPT’s default model to better support those in distress. However, debates around the appropriateness of using ChatGPT for mental health advice continue.
Why do people use ChatGPT as a search engine?
Over half of users state that they use ChatGPT as a search engine over traditional search engines, as it summarises complex topics well.
Most popular reasons for using ChatGPT as a search engine

| Reason | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Summarises complex topics well | 54 |
| Fewer clicks | 33 |
| Feels less cluttered than traditional search | 29 |
| Feels more personal or conversational | 26 |
| More fun or engaging to use | 23 |
| Faster than Google | 18 |
| Easier to use than Google | 10 |
| Feels more trustworthy or unbiased | 7 |
(Source: Adobe Study)
The majority of reasons for using ChatGPT as a search engine relate to its ability to reduce the amount of effort required when searching. A third cite the need for fewer clicks, while three in 10 argue that it feels less cluttered than traditional search, making it easier to find the right information.
How does user satisfaction compare between ChatGPT and traditional search engines?
ChatGPT achieves higher satisfaction rates across five different subject areas than its traditional search engine counterparts.
Consumer satisfaction with results across search engine platforms

| Percentage of respondents who are very satisfied with the results produced when searching for: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | Content topic | Food/recipes | Instructions/how-to... information | News/current events | Product information | Sports and fitness |
| ChatGPT | 33 | 30 | 31 | 33 | 34 |
| Bing | 30 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 29 |
| 27 | 24 | 26 | 26 | 25 | |
| MSN/Microsoft News | 25 | 24 | 26 | 30 | 29 |
| Yahoo | 24 | 21 | 26 | 25 | 25 |
| DuckDuckGo | 23 | 20 | 22 | 20 | 26 |
(Source: GWI)
When comparing ChatGPT and Google, the starkest difference is in the sports and fitness area. While over a third of ChatGPT users are satisfied with the tool’s results in this area, only a quarter of Google users are happy with the engine’s results.
Generative engine optimisation statistics
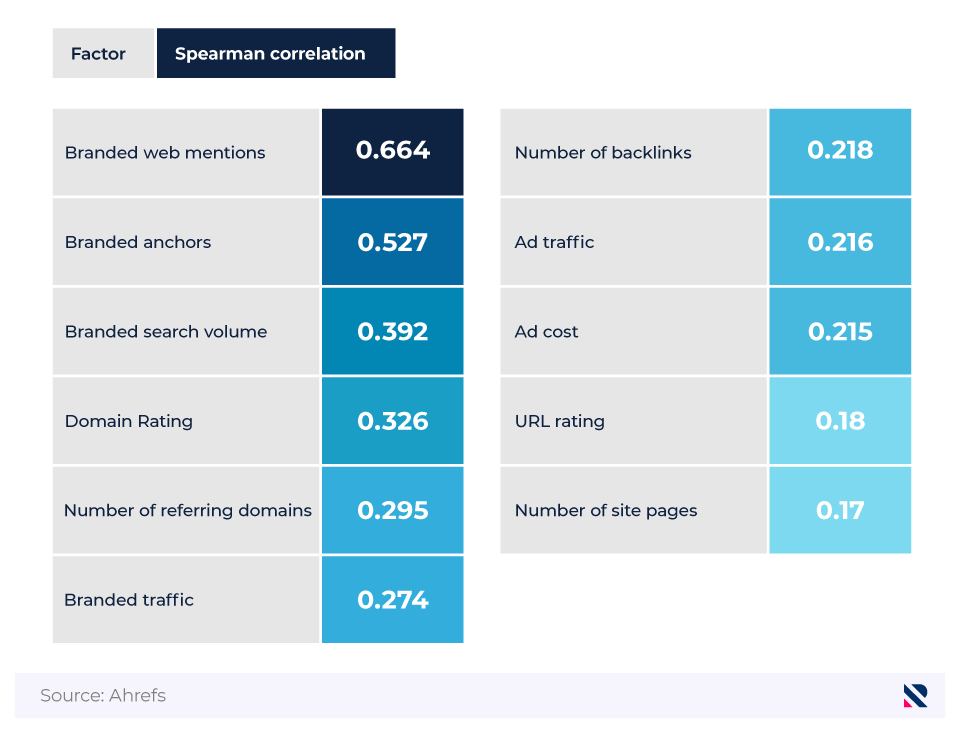
What site factors can impact your AI overview visibility?
According to a study completed by Ahrefs, branded web mentions are the greatest off-site correlation in ensuring brand visibility in AI overviews.
This is an intuitive finding for those working within the generative engine optimisation industry, many of whom have come from working previously in the search engine optimisation space where backlinks and brand authority is the main driver of rankings and SEO visibility.
Below Oliver Sissons, Search Director at GEO agency Reboot Online, shared his thoughts on how and why branded web mentions play such a key role in driving AI visibility:
“In many areas of marketing, it is easy to control the narrative. For example, marketers often have full control over the narratives and claims made in the content published on their own websites, and the other web properties that they own and control. For this reason, AI models simply can’t take the word of marketers and brands as inherently accurate. They are, of course, interested in presenting their brand in the best possible light. Consequently, claims made online must be verified and corroborated across trustworthy sources, and AI models need to look holistically across the web to build up their own understanding of and opinions on various topics, brands, individuals, and entities. This is why web mentions, and historically backlinks in the context of SEO, remain such a key source influence in determining the visibility and sentiment associated with brands online.”
Factors that correlate with brand appearance in AI overviews
| Factor | Spearman correlation |
|---|---|
| Branded web mentions | 0.664 |
| Branded anchors | 0.527 |
| Branded search volume | 0.392 |
| Domain Rating | 0.326 |
| Number of referring domains | 0.295 |
| Branded traffic | 0.274 |
| Number of backlinks | 0.218 |
| Ad traffic | 0.216 |
| Ad cost | 0.215 |
| URL rating | 0.18 |
| Number of site pages | 0.17 |
(Source: Ahrefs)
Branded anchors and branded search volumes also return higher correlation with AI overviews.
Ad spending appears to be less important than the various types of branded data, with both only scoring a Spearman correlation of under 0.220.
What are the most popular GEO strategies?
Among marketers who are focusing on GEO strategies, publishing data-driven content is the most popular method for boosting visibility in AI tools.
Popular strategies used to boost visibility in AI tools
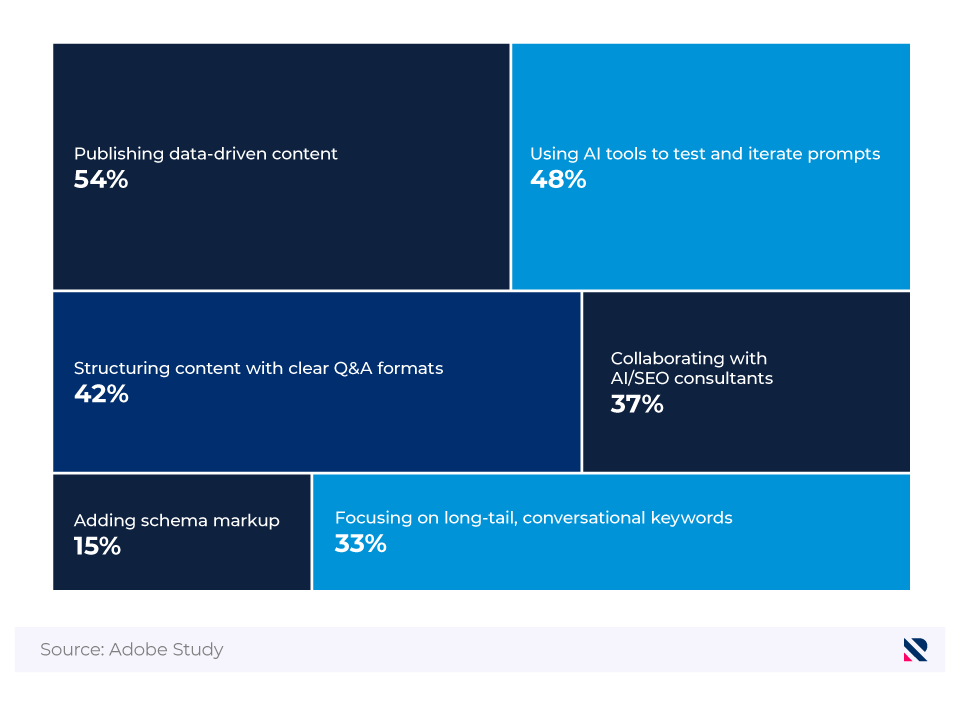
| Strategy | Percentage of respondents |
|---|---|
| Publishing data-driven content | 54 |
| Using AI tools to test and iterate on prompts | 48 |
| Structuring content with clear Q&A formats | 42 |
| Collaborating with AI/SEO consultants | 37 |
| Focusing on long-tail, conversational keywords | 33 |
| Adding schema markup | 15 |
(Source: Adobe Study)
Keywords, a mainstay of traditional SEO strategies, are less popular among marketers, with only a third focusing on long-tail, conversational keywords in their work.
As a GEO agency, Reboot Online has done extensive research into how generative AI has changed the way people search and what this means for brands. The findings, including a blueprint to increase AI citations, can be found in Reboot’s GEO Playbook.
GEO and AI Search glossary
GEO
Generative engine optimisation is the practice of optimising content, and it’s more likely to appear in responses generated by AI-powered search engines. This would include Google’s AI Overviews, Bing’s Copilot, and ChatGPT. Similar to search engine optimisation (SEO), GEO focuses on structuring information so that AI models can understand it and surface it effectively. If you need help enhancing your visibility across generative engines, speak with our GEO agency team.
AI Search
This includes AI tools, including natural language processing, machine learning, and semantic search, to shape how information is retrieved.
Unlike traditional keyword-based search, AI Search understands context, intent, and meaning, providing more accurate, relevant, and personalised results.
LLM
In the context of search, large language models are an AI component that interprets queries and generates responses.
Instead of only matching keywords, LLMs analyse intent and context, then synthesise information from multiple sources into a coherent, human-like answer - such as what appears in AI Overviews.
AI Overview
An AI Overview is Google’s feature that generates a summarised, AI-written answer at the top of the search engine results page (SERP).
It uses generative AI to pull together information from across the web, giving users a quick, synthesised overview instead of a list of links.
Sources
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/state-of-ai/
https://offers.hubspot.com/ai-marketing
https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/2025-state-of-marketing-ai-report
https://www.bain.com/insights/goodbye-clicks-hello-ai-zero-click-search-redefines-marketing/
https://www.adobe.com/express/learn/blog/chatgpt-as-a-search-engine
https://www.gwi.com/blog/ai-and-search
https://ahrefs.com/blog/ai-overview-brand-correlation/
https://openai.com/index/strengthening-chatgpt-responses-in-sensitive-conversations/
Methodology
To determine AI’s impact on salaries in the marketing industry, Reboot Online scraped UK job listings from Indeed, Google, and Glassdoor. Roles analysed included those in marketing, SEO, content, social media, PR, and creative roles.
Listings were reviewed for AI and GEO terms, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, ChatGPT, GPT-4, LLM, prompt engineering, generative AI, and related model or tool names. GEO terms identified included search generative engine optimisation, generative experience, AI overviews, answer engine optimisation, Bing Copilot answers, and similar.
Salaries were calculated by converting weekly, monthly, and hourly pay to estimated annual amounts.
These salaries were then compared across roles that mentioned AI/GEO vs. those that did not.
Sources: https://www.glassdoor.co.uk/index.htm, https://www.google.com/, https://uk.indeed.com/
